| Product Name | β-Nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide Reduced form disodium salt |
| Other names | Coenzyme I reduced disodium salt, β-NADH, CoEnzyme 1, co-e1, codehydrogenase 1,B-DPNH, BNADH, Coenzyme 1, Enada, NAD, Nicotinamide Adénine Dinucléotide, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrate, Reduced DPN, Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. |
| CAS Number | 606-68-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C21H27N7O14P2・Na2 |
| Molecular Weight | 709.4(as disodium anhydrate) |
| Benefits | For energy & Mental Alertness |
| Appearance/color | White to yellowish powder |
| Dosage | 10mg to 50mg |
What is NADH?
NADH is one of Herb Nutritionals Co., Ltd’s novel ingredients on the market with bulk quantity supply. NADH, according to Wikipedia, stands for “nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H)”, one of the most important coenzymes in the human brain and body. NADH is the reduced form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) with High Energy Hydrogen (H) which reacts with the oxygen present in our cells to produce energy. When the body is deficient in NADH, it is like a car that has run out of petrol – it doesn’t go very far or very fast! In essence, the more NADH we have, the more energy we and our cells can produce! NADH is the driving force of cellular energy production.
NADH is the reduced form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) with High Energy Hydrogen (H) which reacts with the oxygen present in our cells to produce energy. When the body is deficient in NADH, it is like a car that has run out of petrol – it doesn’t go very far or very fast! In essence, the more NADH we have, the more energy we and our cells can produce! NADH is the driving force of cellular energy production.
Relation between NADH and NAD
The interconversion of NAD between the reduced (NADH) and oxidized (NAD+) forms is a common reaction in biological redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions. In cells, most oxidations are accomplished by the removal of hydrogen atoms. Each molecule of NAD+ can acquire two electrons; that is, be reduced by two electrons. However, only one proton accompanies the reduction. The other proton produced as two hydrogen atoms are removed from the molecule being oxidized is liberated into the surrounding medium. For NAD, the reaction is thus:
NAD+ + 2H -> NADH + H+
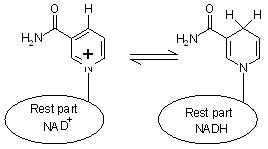
NAD and NADH are converted into each other in numerous different metabolic activities. In some metabolic reactions it is NAD which is the needed catalyst, with NADH a useful by-product, in other reactions the situation is reversed.
NAD and NADH also serve to activate various enzymes, NAD for example, activates alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase that are the two enzymes needed to detoxify the alcohol we drink into carbon dioxide and water.
NADH is the first of five enzyme complexes of the electron transport chain, where much of the ATP bioenergy that runs every biological process of our lives is formed.
Mechanism of action of NADH
As a coenzyme, NADH participates in many biochemical reactions in the body. It is required for the manufacture of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal source of energy for all cellular functions. In the brain, NADH plays an important role in the production of vital neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinepherine, and epinepherine.

Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) is a substance that helps the functionality of enzymes in the body. NADH plays a role in the production of energy and helps produce L-dopa, which the body turns into the neurotransmitter dopamine. NADH is being evaluated for many conditions and may be helpful for enhancing mental functionality and memory.
NADH has energy stored in its chemical structure. When it is absorbed and taken up by the body cells, NADH produces energy. NADH can be compared to a turbine in an electric power plant. Water at a higher level has more energy than water at a lower level. If you insert a turbine (wheel) in this waterfall, you can produce electrical energy. Hence, the more NADH a cell has available, the more energy can be produced. The amount of NADH a cell contains depends on the amount of energy the cell requires. Heart muscle cells have the highest NADH content because the heart is the organ that needs the most energy in the body. Cells in the brain and muscles contain 60 percent of the NADH content of those in the heart。
How does it work?
NADH produced by our bodies is involved in making energy in the body. While there is some evidence that suggests NADH supplements might reduce blood pressure,lower cholesterol, help chronic fatigue syndrome by providing energy, and increase nerve signals for people with Parkinson’s disease, there isn’t enough information to know for sure how or if these supplements work.
Benefits of taking NADH supplement
Health Applications
Energy enhancement
Neurological health
Fatigue
NADH was introduced to the US health market in 1995. There are claims that it can improve memory, athletic performance, slows the aging process, and is helpful in a variety of conditions including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, and overall lack of energy.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), Fibromyalgia, Parkinsons, Alzheimers, Depression, Jet Lag, ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder), and more. What was commonly used to help relieve symptoms of conditions resulting in lack of energy, is now used by athletes, executives, and everyday people to increase energy, improve mental clarity, and improve physical performance.
Energy
NADH is an excellent energy supplement that plays a key role in the energy production of cells, particularly in the brain, the central nervous system and the muscles (remember your heart is a muscle). In simple terms, the more NADH a cell has available, the more energy it can produce to perform its processes efficiently and the longer it survives.
Natural Cellular Stimulation
NADH is an excellent energy supplement that plays a key role in the energy production of cells, particularly in the brain, heart, muscles and central nervous system. The more NADH a cell has, the more energy that cell has allowing it to perform its processes efficiently.
NADH stimulates cellular production of the neurotransmitters dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin, thereby improving mental clarity, alertness and concentration,
helping with depression and giving your body the energy it needs to carry out day to day activities. NADH is directly involved in the body’s cellular immune defensive system and the more NADH in your body, the better the DNA repair system functions.
NADH is involved in over 1,000 metabolic actions in the body, it is necessary for thousands of biochemical reactions within the body and is found naturally in every living cell. It is not a stimulant or a sedative, so it won’t leave you nervous and jittery like caffeine, NADH is just a natural, cellular energy enhancer.
A Potent Antioxidant
Free radicals have been shown to be involved in the development of cancer, coronary disease, atherosclerosis, diabetes, neurodegenrative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, and other autoimmune diseases.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. “Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and diseases”. Biochem J. 1984; 219: 1-14
Cranton EM and Frackelton JP. “Free radical pathology in age associated diseases: Treatment with EDTA chelation, nutrition and antioxidants”. J.Hol:Med. 1984; 6: 6-36.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. “Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: An overview.” Methods Enzymol. 1990; 186: 1-85.
Well known antioxidants are vitamins A, C and E, selenium and glutathione, and as NADH has the highest reducing (antioxidation) power of ANY biological material, it can regenerate spent or used up antioxidants back into their active format. The more free radicals present in a cell, the more damage the cell suffers. This leads to earlier cell death which of course contributes to premature cell and tissue degeneration.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. “Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and diseases”. Biochem J. 1984; 219: 1-14
Cranton EM and Frackelton JP. “Free radical pathology in age associated diseases: Treatment with EDTA chelation, nutrition and antioxidants”. J.Hol:Med. 1984; 6: 6-36.
It is vital that the body has a sufficient supply of free radical antioxidant scavengers to eliminate these free radicals. Again, one of the most potent antioxidants and free radical scavengers is NADH.
We are now aware that the older we get the less NADH we absorb and therefore the elderly are much more vulnerable to free radical damage.
Gutteridge JMC, Halliwell B. Antioxidants in Nutrition, Health and Disease. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1994.
The more NADH they have available in their body, the better the opportunity is for maintaining their health.
Weight Loss
NADH stimulates tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) which is the key enzyme for the production of Dopamine, up to 70%.
Vrecko K, Birkmayer JGD, Krainz J. “Stimulation of dopamine biosynthesis in culture P12 pheochromocytoma cells by the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH)”. J.Neural. Transm. 1993;5:147-156
Dopamine is one of the factors in controlling a person’s appetite, the higher the dopamine level the lower the appetite. This may be of particular interest to those overweight individuals.
Cholesterol
In a double blind trial it was demonstrated that NADH lowered the cholesterol level in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Cholesterol levels were reduced by 30% after 10 weeks of treatment.
Busheri N, Taylor J, Lieberman S, Mirdamadi-Zonosi N, Birkmaye¡r G, Preuss HG. “Oral NADH affects blood pressure, lipid peroxidation and lipid profile in spontaneously hypersensitive rats”. J Am Coll Nutr. 1997, in print.
These preliminary studies will help determine the applicability for longer term human studies using NADH.
Blood Pressure
The same trial showed the positive reduction in blood pressure again demonstrating the potential that NADH has.
Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s disease is characterised by 3 main things, tremors, rigidity and akinesia (inability to move). The organic cause of this disease lies in the brain where damage is caused to one of the most important messenger substances of the central nervous system, dopamine. This neurotransmitter is responsible for muscle tone, upright position, muscle strength, libido and emotional drive.
The classical treatment for Parkinson’s is Simemet which is L-Dopa combined with a decarboxylase inhibitor. The treatment is a pure substitutional therapy designed to resupply dopamine due to insufficient levels in the brain. By taking L-Dopa, many patients are relieved of their symptoms however, there are drawbacks. First of all, this therapy stops the body’s own production of L-Dopa due to a “feedback inhibition” mechanism. The other main drawback is that because the L-Dopa is provided in unphysiologically high amounts, the dopamine is oxidised forming enormous amounts of damaging free radicals.
Many studies have shown that NADH is able to naturally stimulate the production of Dopamine with none of the aforementioned drawbacks. In an open-label clinical trial, 885 Parkinsonian patients were treated with NADH and a significant number improved their mobility, walking, posture and speech. This was confirmed by a double blind study conducted at the University Clinic in Germany. Researchers there found that not only did patients’ disability improve, but also their levels of L-Dopa and dopamine were significantly increased.
KuhnW, Muller Th, Winkel R, Danielczik S, Gerstner A, Hacker R, Mattern C, Przuntek H,. “Parenteral application of NADH in Parkinson’s disease: clinical improvement partially due to stimulation of endogenous levodopa biosynsthesis.” J.Neural. Transm. 1996; 103: 1187-1193
Alzheimer’s / Dementia
Dementia can be defined as loss of intellectual functions such as thinking, remembering and reasoning of sufficient severity to interfere with a person’s daily functioning. It is not really a disease but a variety of symptoms.
In an open label trial, patients, who all had been clinically diagnosed as having pre-senile and senile dementia were provided with NADH. After a 3 month treatment period, an improvement as measured by the USA’s Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the Global Deterioration Score (GDS) could be observed. On the basis of this, an FDA approved clinical study of NADH was launched and NADH was shown to improve cognitive impairment in a double blind, placebo controlled study performed at Georgetown University Medical Center. Patients showed statistically significant improvement after 6 months treatment with NADH.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome / Fibromyalgia
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome is characterised by a combination of various symptoms and complaints, not necessarily related. A possible cause is the depletion of the cellular energy storage molecule ATP.
The precise cause of CFS is unknown (Calabrese et al., 1992). Symptoms include prolonged and debilitating fatigue, inability to concentrate, flu-like symptoms, muscle weakness, joint pain, headaches, and sleep disturbances (Chester, 1997; Komaroff and Buchwald, 1991). CFS affects about 500,000 Americans, but no effective treatment is known (Gantz and Holmes, 1989; Houde and Kampfe-Leacher, 1997). Researchers theorize that CFS stems from a lack of the chemical responsible for cellular energy, ATP (Klonoff, 1992). One theory is that both infections and stress deplete cellular ATP levels and lead to chronic fatigue, and that supplemental levels of NADH can stimulate ATP production and provide benefits to people suffering from fatigue and cognitive dysfunction (Colquhoun and Senn, 2000). Further benefits from NADH may stem from its role in stimulating the production of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine (involved in brain function and memory) as well as from the stimulation of tyrosine hydroxylase, an enzyme involved in synthesizing neurotransmitters (Birkmayer el al., 2002).
In the two existing well-controlled studies of NADH supplementation, 10-20 mg of NADH showed some promising antifatigue effects. In one study (Forsyth et al., 1999),10 mg/day of NADH for 4 weeks was effective in alleviating generalized symptoms of CFS in about one third of patients.
A study was conducted at the Georgetown University stating that four times more patients showed an improvement in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome symptoms after NADH compared to a placebo.
L.M. Forsyth, MD; A.L. MacDowell-Carnciro, MD; G.D. Birkmayer, MD, PHD; H.G. Preuss, MD; and J.A. Bellanti, MD; departments of Pediatrics and Microbiology-Immunology and the Immunology Center, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, DC . Published February 1999; issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.
Depression
Depression is a neuropsychiatric disorder. A number of studies revealed that certain neurotransmitters, in particular adrenaline, dopamine, serotonin and their metabolites play a role in the evolving depression symptoms.
NADH was used in an open label trial as medication in 205 patients suffering from depression with various clinical symptoms. The duration of the trial lasted from 5 to 310 days with 93% of the patients exhibiting a beneficial clinical effect. An improvement up to 44% with a mean value of 11.5 was observed.
Birkmayer GD, Birkmayer W. “The coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) as biological antidepressive agent experience with 205 patients.” New Trends in Clinical Neuropharmacology 1991; 5: 75-86.
Anti-Aging
As we age, the NADH and energy levels in our cells decrease.
Stocchi V, Kolb N, Cucchiarini L, Segni M, Magnani M, Fornaini G. “Adenine and pyridine nucleotides during rabbit reticulocyte maturation and cell aging.” Mechanisms of aging & Development 1987; 39: 29-44.
When the cellular energy declines below a certain threshold the cell dies and the tissue degenerates. However, if the energy productions in the organs and cells can be kept at the same levels as that of a younger person, this may translate to feeling younger, being more active and looking better than the actual biological age would indicate.
Athletes
NADH supplementation is 100% legal for athletes therefore no doping worries.
In 1995, a study was conducted among competitive level cyclists and long distance runners. A significant range of performance improvements were recorded. These included an increase in their ATP energy levels by 7%, increase in their blood oxygen levels, a decrease in their reaction times, decrease in their lactic acid and decrease in their recovery times.
More recently, a study was done with a European champion football team. Blood samples were taken before and after the 4 week treatment period. The L-Dopa blood level increased in all the athletes by between 30 and 100%. L-Dopa is instantly converted to the neurotransmitter dopamine and dopamine is responsible for muscle strength, instinct movements, spontaneous reactions, libido and emotional drive. All but 3 increased their noradrenaline levels. Noradrenaline increases vigilance, alertness, concentration and stress capacity.
If professional and top flight athletes can achieve these improvements, think what it could do for the “weekend warrior”?
Immune System
The immune system is based on the activities of our white blood cells.
One of the main white blood cell sub-groups is macrophages. Macrophages are responsible for the direct elimination of bacteria or viruses. There is a direct relationship between the intake and digestion process of the macrophages and the activation of the immune system. When bacteria or viruses enter the body, the metabolic activity of macrophages causes an increase in oxygen consumption. Oxygen is converted to superoxide which destroys these bacteria and viruses. During this oxygen demand, high amounts of NADH are consumed. Hence the more NADH that is available, the better the immune system works.
CoEnzyme Q10
NADH is also vital in making the popular supplement Coenzyme Q10 behave as an effective antioxidant – a fact not often understood by the majority of Coenzyme Q10 users.
Coenzyme Q10 is used to treat migraines, heart failure, gum disease, Parkinson’s disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. However, it is only when Coenzyme Q10 is combined with NADH that it become effective and beneficial to the body. If the body has insufficient amounts of NADH, CoQ10 will deplete the NADH which has the double negative of making you extremely tired and also, the remainder of the CoQ10 ineffective. Sufficient NADH is required to alter CoQ10 into an antioxidant and an energy producing compound.
Side effects of taking NADH supplements
It is not a stimulant or a sedative, so it won’t leave you nervous and jittery like caffeine, NADH is just a natural, cellular energy enhancer.
Dosage of NDAH
The appropriate dose of NADH depends on several factors such as the user’s age, health, and several other conditions. The most commonly recommended dose for NADH is 10 mg per day, but clinical studies on NADH have used up to 50 mg per day with no significant side-effects. Although studies have shown no toxic effects with up to a year or more of use, the safety of long-term NADH use has not been evaluated.
