Bulk flavin mononucleotide
| Product name | Flavin mononucleotide |
| Synonyms | riboflavin-5′-phosphate,FMN, riboflavin phosphate,[(2R,3S,4S)-5-(7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxobenzo[g]pteridin-10-yl)-2,3,4-trihydroxypentyl] hydrogen phosphate |
| CAS Number | 146-17-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C17H21N4O9P |
| Molecular Weight | 456.344 |
| Solubility | Water soluble |
| Specifications | 99% |
| Appearance | yellow to orange crystalline powder |
| Benefits | Coenzymes, Overall health,food color additive |
| Applications | Supplements, nutrition,food additives |
| Dosage | 20mg daily |
| Package | 25kg/drum |
What is flavin mononucleotide?
The definition of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) can be summarized that it is a a derivative of riboflavin consisting of a three-ring system (isoalloxazine) attached to analcohol(ribitol),acting as a coenzyme for a number of oxidative enzymes, including NADH dehydrogenase, l-amino acid oxidase and cytochrome C reductase. FMN is the main active form of riboflavin (vitamin B2).
According to Wikipedia, during catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs in the various oxidoreductases. FMN is a stronger oxidizing agent than NAD.
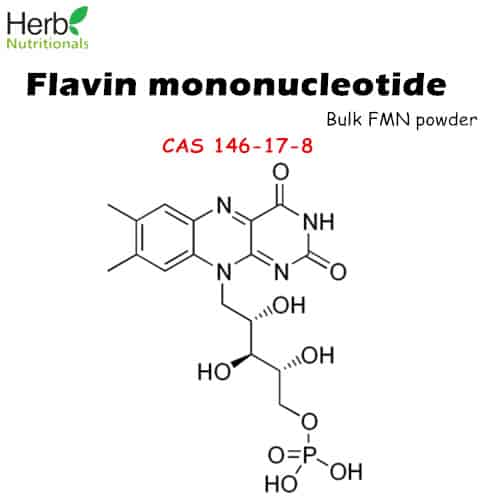
Flavin mononucleotide has many other names, known as FMN, riboflavin-5′-phosphate, with the molecular formula C17H21N4O9P and the unique CAS number 146-17-8.
Riboflavin vsFMN vs FAD
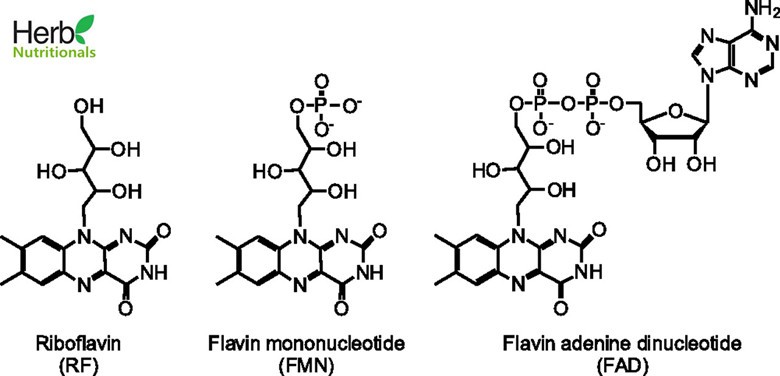
Flavin is the common name for a group of organic compounds based on pteridine, formed by the tricyclic heterocycle isoalloxazine. The biochemical source is the vitamin riboflavin. The Latin name of Flavin is flavus, meaning the color of “yellow”. That’s also why most flavins are in yellow powder color.
Flavins are ubiquitous in nature and take part in many biochemical reactions mainly in the form of the coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), which function as redox cofactors in different flavoproteins.
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is a yellow-colored nutrient involved in dozens of metabolic pathways leading to energy production and the making of fatty acids and sterols. Riboflavin is part of two larger activated coenzymes known as flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavin mononucleotide (FMN). FMN is now available as a supplement. One product contains 25 mg of FMN per pill.
Riboflavin is utilized by the liver, brain, heart and other tissues to synthesize flavine mononucleotide (FMN) and flavine adenine dinucleotide (FAD), the active forms of riboflavin. These coenzymes play major roles in energy production; cellular function, growth, and development; and metabolism of fats, drugs, and steroids. The conversion of the amino acid tryptophan to niacin (sometimes referred to as vitamin B3) requires FAD. Similarly, the conversion of vitamin B6 to the coenzyme pyridoxal 5′-phosphate needs FMN. In addition, riboflavin helps maintain normal levels of homocysteine, an amino acid in the blood.
More than 90% of dietary riboflavin is in the form of FAD or FMN; the remaining 10% is comprised of the free form and glycosides or esters. Most riboflavin is absorbed in the proximal small intestine. The body absorbs little riboflavin from single doses beyond 27 mg and stores only small amounts of riboflavin in the liver, heart, and kidneys. When excess amounts are consumed, they are either not absorbed or the small amount that is absorbed is excreted in urine.
Flavin adenine dinucleotide and flavin mononucleotide
Flavin adenine dinucleotide(FAD) and flavin mononucleotide(FMN) are the active form of riboflavin, which is also popularly known as Vitamin B2. In other word, riboflavin is the precursor of flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide, and part of the vitamin B complex. Flavin mononucleotide is itself the precursor for the other B-2 coenzyme, flavin adenine dinucleotide. In this way, flavin mononucleotide can convert into Flavin adenine dinucleotide under necessary situations.
As the water solubility or absorption is concerned, flavin mononucleotide is better than free riboflavin, and better than flavin adenine dinucleotide. The free riboflavin is even better than flavin adenine dinucleotide in this solubility aspect. At this moment, we find that FMN supplement is readily available, while flavin adenine dinucleotide supplements are not found anywhere.
Mechanism of action of flavin mononucleotide
In order for vitamins to be utilized by the body, they must first be converted into their active coenzyme forms. Flavin mononucleotide goes directly into your bloodstream in its active form, ready to go to work immediately. This avoids loss that may occur not only during digestion, but during the liver’s conversion process as well. Flavin mononucleotide (FMN), also called riboflavin phosphate, is one of the two metabolically active coenzyme forms of vitamin B-2. FMN is involved in a wide array of enzymes and has many roles in energy production from our food, as well as bio-converting B-6 to its coenzyme form.
FMN and FAD are cofactors for a variety of oxidative enzyme systems and function as electron carriers important for the synthesis of energy (ATP). FAD is also involved in the activation of folate, the metabolism of neutrotransmitters, and regeneration of reduced glutathione. Alcohol reduces digestion and absorption of riboflavin. Riboflavin also supports the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Function and Mechanism of Action FMN and FAD function as coenzymes for a wide variety of oxidative enzymes and remain bound to the enzymes during the oxidation-reduction reactions. Flavins can act as oxidizing agents because of their ability to accept a pair of hydrogen atoms. Reduction of isoalloxazine ring (FAD, FMN oxidized form) yields the reduced forms of the flavoproteins (FMNH2 and FADH2). Flavoproteins exhibit a wide range of redox potential and therefore can play a wide variety of roles in intermediary metabolism. Some of these roles are:
* Flavoproteins play very important roles in the electron transport chain
* Decarboxylation of pyruvate and α-Ketoglutarate requires FAD
* Fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase requires FAD in fatty acid oxidation
* FAD is required to the production of pyridoxic acid from pyridoxal (vitamin B6)
* The primary coenzyme form of vitamin B6 (Pyridoxal phosphate) is FMN dependent(5)
* FAD is required to convert retinal (Vitamin A) to retinoic acid
* Synthesis of an active form of folate (5-methyl THF) is FADH2 dependent
* FAD is required to convert tryptophan to niacin (vitamin B3)
* Reduction of the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) to its reduced form (GSH) is also FAD dependent
Flavin mononucleotide Benefits
The benefits of flavin mononucleotide can be summarized as the riboflavin benefits, but much more potent and effective.
Since riboflavin and their coenzymes play important metabolic roles in numerous biochemical reactions throughout the body, they can influence just about every aspect of brain and physical health. As a rule, individuals who take riboflavin notice improvements in:
Mood and energy
Alertness and mental stamina
Learning and memory
Speed of thinking
Verbal fluency
Concentration and focus
Visual clarity
Flavin mononucleotide is also used as an orange-red food color additive, designated in Europe as E number E101a. E106, a very closely related food dye, is riboflavin-5′-phosphate sodium salt, which consists mainly of the monosodium salt of the 5′-monophosphate ester of riboflavin. It is rapidly turned to free riboflavin after ingestion. It is found in many foods for babies and young children as well as jams,milk products, and sweets and sugar products.
Flavin mononucleotide side effects
There is no much enough safety data for flavin mononucleotide. However, as the active ingredient of riboflavin which is a water-soluble vitamin, FMN is believed to be safe as a supplement. Even take excess amounts of FMN supplements, it is safe and the FMN can be easily excreted by the body in the urine. If there is any adverse effects, please contact your doctor for emergent help.
Flavin mononucleotide dosage
Flavin mononucleotide is relatively new to the dietary supplement market, and there is no recommended dosage for flavin mononucleotide (FMN). We may compare FMN with riboflavin, which is a mature ingredient and many studies and researches have been made upon its dosing.
Riboflavin, for the purpose of maintaining a sufficient riboflavin status in the body, can be supplemented at a relatively low dose of 1-2mg daily to support riboflavin stores in the body. Higher dose (4mg) may increase stores more rapidly but may perform equally over the long term, and these doses are also what should be taken for the purpose of reducing homocysteine concentrations.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), as a supplement, is usually included in multivitamins and B-complex vitamins, available separately in doses of 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg. About 95% of riboflavin in the form of FAD or FMN from food is bioavailable up to a maximum of about 27 mg of riboflavin per meal or dose.
According to the Flavin mononucleotide supplements available on the market, the dose for flavin mononucleotide tablet is 18mg from 25mg flavin mononucleotide Coenzymated™, which is obviously more efficient than riboflavin.
Where to buy bulk Flavin mononucleotide powder?
Herb Nutritionals Co., Ltd probably is the first manufacturer of bulk flavin mononucleotide powder in China. Make sure that our flavin mononucleotide ingredient is in powder form, not finished FMN supplements in bottle. Supplements brands and contracting manufacturing factories are our targeted clients. If you need to know the prices, technical documents such as COA(certificate of analysis), MSDS(Material Safety Date Sheet), specifications of our flavin mononucleotide, please feel free to send us an email to get a quote. We will get you replied within 12 hours.
