Benfotiamine 99%
| Product name | Benfotiamine 99% |
| Synonyms | Milgamma, S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate, benfotiamina, benfotiamin, BenfoPure, BenfoMax, allithiamine, S-benzoylthiamine-O-monophosphate, benphothiamine |
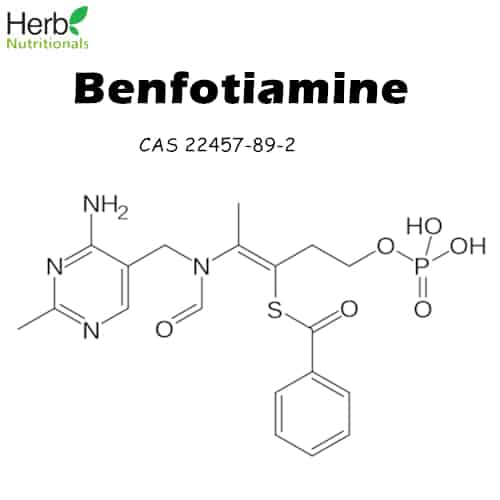
| CAS number | 22457-89-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N4O6PS |
| Molecular Weight | 466.448 |
| Specifications(assay) | 98%,99% |
| Appearance/color | White crystalline powder |
| Solubility | lipid-soluble(fat soluble) |
| Package | 25kg/drum |
| Benefits | Diabetes, blood sugar control, brain health, sciatica |
| Applications | Dietary supplements,drugs |
| Dosage | 150mg or 300mg twice daily |
What is benfotiamine?
Benfotiamine, synthetic derivative of thiamine (vitamin B-1), has been on the market since 1993 in Germany under the name of Milgamma combined with pyridoxine as a drug medicine for the treatment of sciatica, back pain, and other painful nerve conditions. However, nowadays supplement is the biggest market for benfotiamine.
Benfotiamine is approved to work in supporting healthy glucose metabolism, helping to blunt the blood insulin-spiking and cell-harmful effects of high sugar consumption. Additionally, benfotiamine has long been proven to aid healthy circulation in capillary vessels, mainly in the limbs where diabetes can wreak a number of its most nasty damage. The detailed benefits is going to be shown within the next part.
Benfotiamine is defined as an odor free, bitter-tasting, white crystalline powder. It’s fat souble,free-flowing and non-hygroscopic so it can be developed into pills or capsules.
Although benfotiamine is not GRAS granted by the FDA, it is surely to get this status in the coming years, since many manufacturers have submitted their documents for this NDI filing process.
Natural sources of benfotiamine
Broadly obtainable in supplement form, benfotiamine, referred to as allithiamines, is identified naturally within the allium genus group of crushed garlic clove, onions, chives, shallots, leeks, along with other vegetables.However, most supplements on the market contain a synthetic form of benfotiamine.
Benfotiamine is made synthetically or perhaps is manufactured by enzymatic synthesis using yeast phosphokinases. Don’t even think of buying natural benfotiamine from the supplement store which is expensive and not feasible.
Benfotiamine vs. Thiamine
General speaking, benfotiamine is more absorbable, and has better bioavailability than thiamine. The comparison details you may refer to the sulbutiamine VS thiamine. Both sulbutiamine and benfotiamine are the derivatives of thiamine (or vitamin B1). Sulbutiamine cross the blood-brain barrier while benfotiamine doesn’t. Benfotiamine is fat soluable while thiamine is water soluable. Your body does make small quantities of benfotiamine from regualar B1, but may not be sufficient if perhaps a little quantity is taken.
Mechanism of action of benfotiamine
Benfotiamine has proven to affect glucose metabolic process through various mode of actions, and plays a part in obstructing age-associated glycation end products (AGEs). Benfotiamine reduces the extra biosynthesis and accumulation of a number of glucose metabolites, including glyceraldeyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Elevated levels of those glucose intermediates function as a trigger to most of the mechanisms accountable for hyperglycemia-caused cell damage. Benfotiamine increases tissue amounts of thiamine diphosphate, consequently growing transketolase activity and producing a significant decrease in glucose metabolites and precursors to AGEs. Up to now, two of the most effective AGE inhibitors in living microorganisms would be the Vitamin B1 derivative, benfotiamine and also the Vitamin B6 derivative, pyridoxamine. Benfotiamine was probably the most potent, that pyridoxamine was less strong as benfotiamine.
Benfotiamine likewise helps lessen the activity of aldose reductase, which helps limit tissue accumulation of sorbitol and glucose, assisting to reduce endothelial cell damage.
Additionally, benfotiamine has long been proven to lessen NF-kB activity, therefore restricting the over-production from the harmful superoxide toxin. Excess superoxide production may partly hinder a vital enzyme in glucose metabolic process, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, directing glucose metabolites from glycolysis in to the major glucose-driven signaling paths that cause hyperglycemic damage.
Benefits of benfotiamine
Benfotiamine is used as dietary supplements in the United States and prescription drugs in the Europe for the treatment of thiamine deficiency, diabetic neuropathy, alcoholic neuropathy, diabetic vascular complications, diabetic retinopathy, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease, diabetic nephropathy, end-stage renal disease, etc.
Benfotiamine and diabeties

benfotiamine diabetes
Based on the American Diabetes Association, you will find an approximately 23.6 million individuals the USA (8% of people) with diabetes. Diabetes drugs are some of the most broadly recommended pharmaceutical drugs currently available. Current medicines for type II diabetes seek to pay attention to establishing bloodstream glucose control within the blood stream by either growing blood insulin production or improving its usefulness, but frequently overlook the necessity to safeguard against common diabetic complications for example blindness, stroke, endothelial disorder, and lack of limb.
However, Benfotiamine has been proven to assist in avoiding the development of many diabetic complications. Benfotiamine improves the advancement of diabetic nerve, kidney, and retinal damage, and relieves the painful signs and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy causes it to be hard for nerves to carry messages to the brain as well as impairs the function of the tiny blood vessels within the limbs.
Benfotiamine and Kidney Health
High Blood Sugar can lead to chronic kidney disease. Kidney disease, or nephropathy, is among the most horrible complications of diabetes. When kidney function drops in individuals with diabetes, the renal system may no more have the ability to perform their crucial task of filtering urine. Consequently, diabetes sufferers with advanced nephropathy must turn to kidney dialysis or perhaps a kidney transplant. Kidney disease also increases the chance of coronary disease and overall mortality.
Benfotiamine and cardiovascular health
Benfotiamine supplements also enhance cellular health and cardiovascular health. Additionally they help to boost nerve health, reduce high bloodstream pressure, treat fibromyalgia syndrome and stop build-from lactic acidity after strenuous activity.
Elevated triglyceride levels and elevation of low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol and depression of high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol. All risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Assists in maintaining normal endothelial function, and structure, which is connected with optimal cardiovascular health.
Benfortiamine and Brain health
As reported by the World Health Organization, high sugar consumption is among the top ten greatest brain damaging habits. Diets full of added sugar can result in a brain condition which can lead to dementia, depression, and diabetes type 2.
Glucose metabolism decreased drastically in brain tissue of patients with Alzheimer’s (AD). This abnormality may precede any brain signs and symptoms by decades. Diabetes, with disturbed glucose metabolism, is really a risk factor for Alzheimer’s.
Although testing continues to be done on benfotiamine and its effects for Alzheimer’s shows promise. Based on a 2010 study publish by Brain, researchers demonstrated that animals given benfotiamine for eight weeks found significant improvement in cognitive function as well as benfotiamine helpedaided to battle the build-from amyloid plaque that has been linked in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Benfotiamine is frequently stated to be helpful in natural treatments for back discomfort, fatigue, fibromyalgia syndrome, and sciatica. It’s also recommended that it may make it possible to slow aging, enhance exercise performance, boost mood and improve brain functions. Benfotiamine can work as an antioxidant to safeguard cells from toxin damage triggered by AGEs – a kind of toxin created by broiling, baking, or grilling meat or any other animal products.
Side Effects of Benfotiamine
When benfotiamine is taken orally, it’s rapidly digested yielding elevated amounts of thiamine pyrophosphate, the standard working type of thiamine in your body.
You will find no reviews of benfotiamine side effects within the medical literature. You will find no reviews of benfotiamine interactions with prescription medications, other vitamins, meals, or supplements.
Theoretically, overdose with benfotiamine should cause menopausal flashes, bluish skin (because of rapid utilization of oxygen), tingling, and difficulty breathing, but used, this merely has not happened.
Benfotiamine dosage
Benfotiamine is generally taken in the dose of 300 to 600mg every day, usually in 2 divided doses with foods (150mg or 300mg two times daily). The exact benfotiamine dosage may vary with assorted condition treatment, such for neuropathy, for kidney repair, diabetes,etc.
You may find that many supplement brands using benfotiamine within two to three weeks at a dosage of two 150 mg taken twice daily. However, you might increase this dosage to 900 mg each day to determine maximum results. You may need to test out your dosage to obtain the level that works well with you.
Where to buy bulk benfotiamine powder ingredient?
Benfotiamine and sulbutiamine are two new ingredients from Herb Nutritionals since 2014. Bulk benfotiamine 99% in powder form is ready stock available. Documents like COA,MSDS, Specifications are obtainable upon your request via email, phone from our contact us page.